Cloud computing has become a core part of how modern businesses run their operations, as Cloud Computing Essentials Unlock Benefits that go beyond basic technology use. Instead of managing costly hardware and complex IT systems, companies now use cloud services to access storage, software, and computing power when needed. This shift helps businesses save time, reduce costs, and stay flexible in a fast-moving digital environment.
Understanding cloud computing essentials is what turns cloud adoption into real value. When businesses know the basics, they unlock benefits like better cost control, improved security, easy scalability, and smoother teamwork. These essentials help leaders make informed decisions and avoid common cloud mistakes.
As digital transformation continues, cloud computing supports growth, remote work, and long-term stability. Businesses that understand cloud fundamentals early are better prepared to adapt, compete, and succeed in today’s digital-first world.
What Are Cloud Computing Essentials?
Cloud computing essentials are the basic concepts and practices that help businesses use cloud technology correctly and safely. These essentials explain how cloud systems work, what services are available, and how organizations can use them without owning or managing physical hardware. When businesses understand these basics, they avoid confusion and make better long-term technology decisions.
At a practical level, cloud computing allows companies to access computing resources through the internet. Instead of setting up local servers, businesses rely on cloud providers to deliver services that are flexible, reliable, and easy to manage. This approach supports growth while keeping IT operations simple and controlled.
Cloud computing essentials also clarify responsibility. Cloud providers manage the infrastructure, but businesses remain responsible for how data, access, and applications are handled. Understanding these essentials helps organizations stay secure, control costs, and align cloud usage with business goals.
Also Read: Data Security in Cloud Computing: Your Complete Guide
Core Cloud Computing Fundamentals Explained Simply
The fundamentals of cloud computing are easy to understand when broken down into clear parts.
- On-demand access
Businesses can use computing resources instantly without long setup or waiting periods. This helps teams respond quickly to changing needs. - Scalability
Cloud systems allow businesses to increase or reduce resources based on demand. Companies only use what they need and avoid paying for unused capacity. - Shared infrastructure
Cloud providers operate large data centers that serve many customers securely. This shared model lowers costs while maintaining performance and reliability. - Pay-as-you-use pricing
Businesses pay only for the resources they consume. This removes large upfront investments and improves budget control. - Remote accessibility
Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This supports remote work and distributed teams.
Why Cloud Computing Essentials Matter in 2026
In 2026, businesses operate in a fast digital environment where speed, security, and flexibility matter more than ever. Cloud computing essentials help companies make smart technology decisions that support growth without adding unnecessary cost or risk.
- Faster adaptation: Cloud systems allow businesses to respond quickly to market changes and customer needs.
- Better cost control: Understanding cloud basics helps companies avoid overspending and use resources efficiently.
- Stronger security awareness: Cloud knowledge helps businesses protect data and manage access responsibly.
- Support for modern work: Cloud platforms enable remote teams, online tools, and flexible workflows.
- Foundation for innovation: Technologies like automation and artificial intelligence depend on cloud infrastructure.
As digital transformation continues, cloud computing essentials are no longer optional. Businesses that understand them are better prepared to stay competitive, protect their operations, and grow with confidence in the years ahead.
How Cloud Computing Essentials Unlock Benefits for Businesses
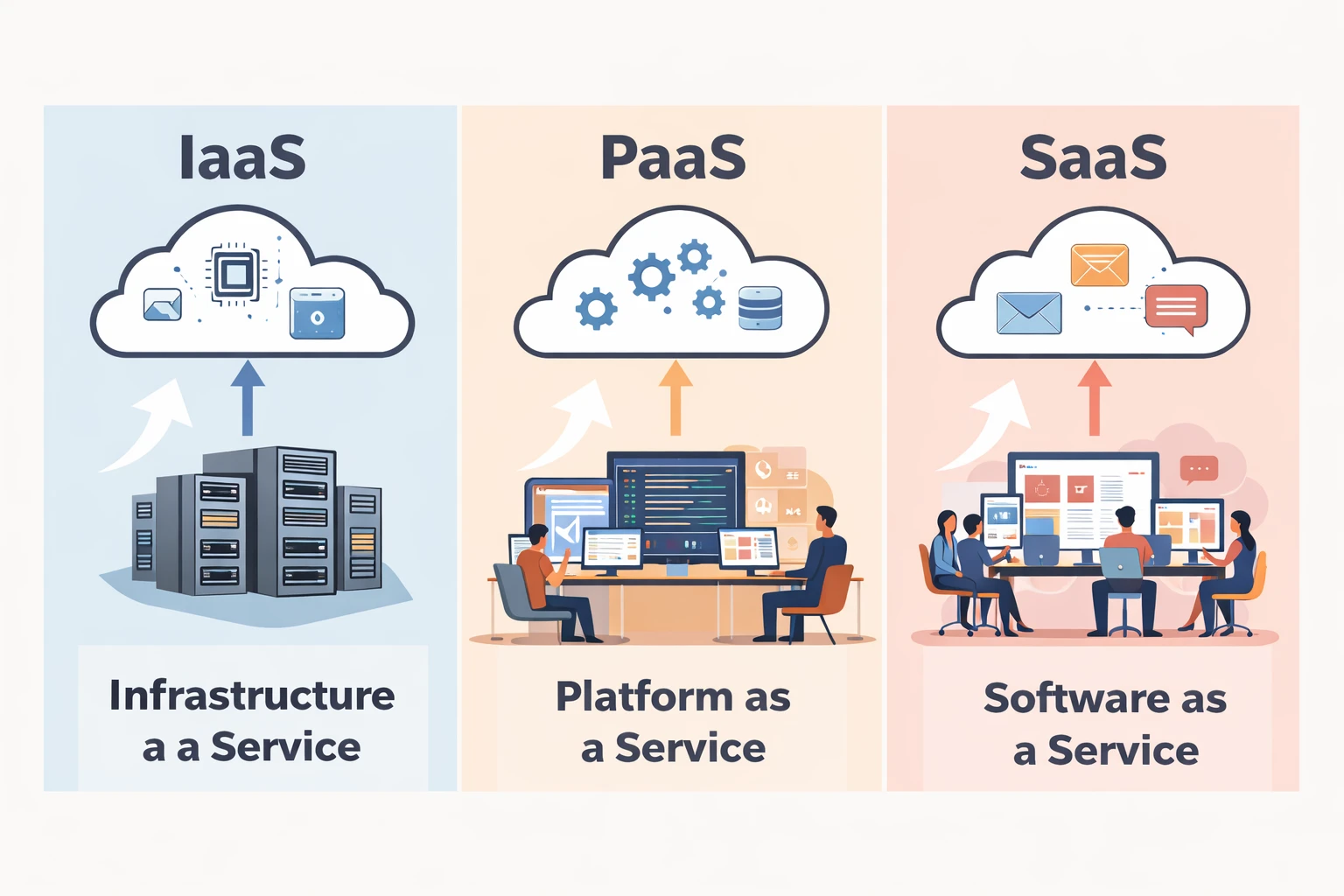
Cloud computing delivers real value when businesses clearly understand its core service models. Infrastructure, platforms, and software each solve different problems. Knowing how and when to use them helps organizations reduce costs, improve performance, and scale without unnecessary risk.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service provides the foundation of cloud computing. It offers virtual servers, storage, and networking through the internet. Businesses no longer need to buy or maintain physical hardware. Instead, they rent computing resources based on their needs.
IaaS is useful for businesses that want control and flexibility. IT teams can configure systems, choose operating systems, and manage applications while the cloud provider handles physical infrastructure.
Key benefits of IaaS include:
- Lower upfront costs by removing hardware purchases
- Easy scaling during high or low demand periods
- Better disaster recovery through cloud backups
- Improved reliability with professionally managed data centers
IaaS is commonly used for hosting websites, running business applications, and managing large amounts of data.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service focuses on application development. It provides a ready-to-use environment where developers can build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about servers, updates, or system maintenance.
PaaS helps businesses move faster. Development teams spend more time writing code and less time managing infrastructure. This improves productivity and reduces delays.
Key benefits of PaaS include:
- Faster application development and deployment
- Reduced technical complexity for development teams
- Built-in tools for testing and performance monitoring
- Easier collaboration between developers
PaaS is ideal for businesses creating custom software, web applications, or digital services.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service delivers complete software applications through the internet. Users access these tools through a browser without installing or updating anything. The cloud provider manages security, updates, and performance.
SaaS is the most common cloud service for everyday business operations. It helps teams work efficiently from any location.
Key benefits of SaaS include:
- Quick access to business tools without setup
- Automatic updates and security management
- Easy collaboration for remote and office teams
- Predictable costs through subscription models
SaaS is widely used for email, customer management, accounting, and team communication.
When businesses understand IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS clearly, they can choose the right tools for the right tasks. This knowledge helps cloud computing essentials unlock benefits such as cost efficiency, flexibility, security, and long-term business growth.
How Cloud Computing Essentials Unlock Real Business Benefits
Cloud computing delivers real results when businesses understand and apply its essentials correctly. These basics help organizations reduce waste, improve performance, and build systems that support daily work without unnecessary complexity. When cloud essentials are used with clear intent, businesses see practical benefits that directly impact growth and stability.
- Cost optimization: Cloud computing helps businesses control IT spending. Companies pay only for the resources they use, avoid large hardware costs, and reduce maintenance expenses.
- Scalability: Cloud systems allow businesses to grow or scale down easily. Resources can be adjusted based on demand without service disruption or long setup times.
- Security: Cloud platforms provide strong security features such as data protection, access control, and regular updates. Understanding cloud basics helps businesses use these features properly and reduce risk.
- Remote work support: Cloud services allow teams to access data and applications from anywhere. This improves productivity and supports flexible work environments.
- Business continuity: Cloud computing helps businesses recover quickly from system failures or disruptions. Data backups and recovery options reduce downtime and protect operations.
When cloud computing essentials are applied correctly, businesses gain more than just technology. They gain control, confidence, and the ability to operate efficiently in a digital world. These benefits make cloud knowledge a key factor in long-term business success.
Cloud Deployment Models Explained for Businesses
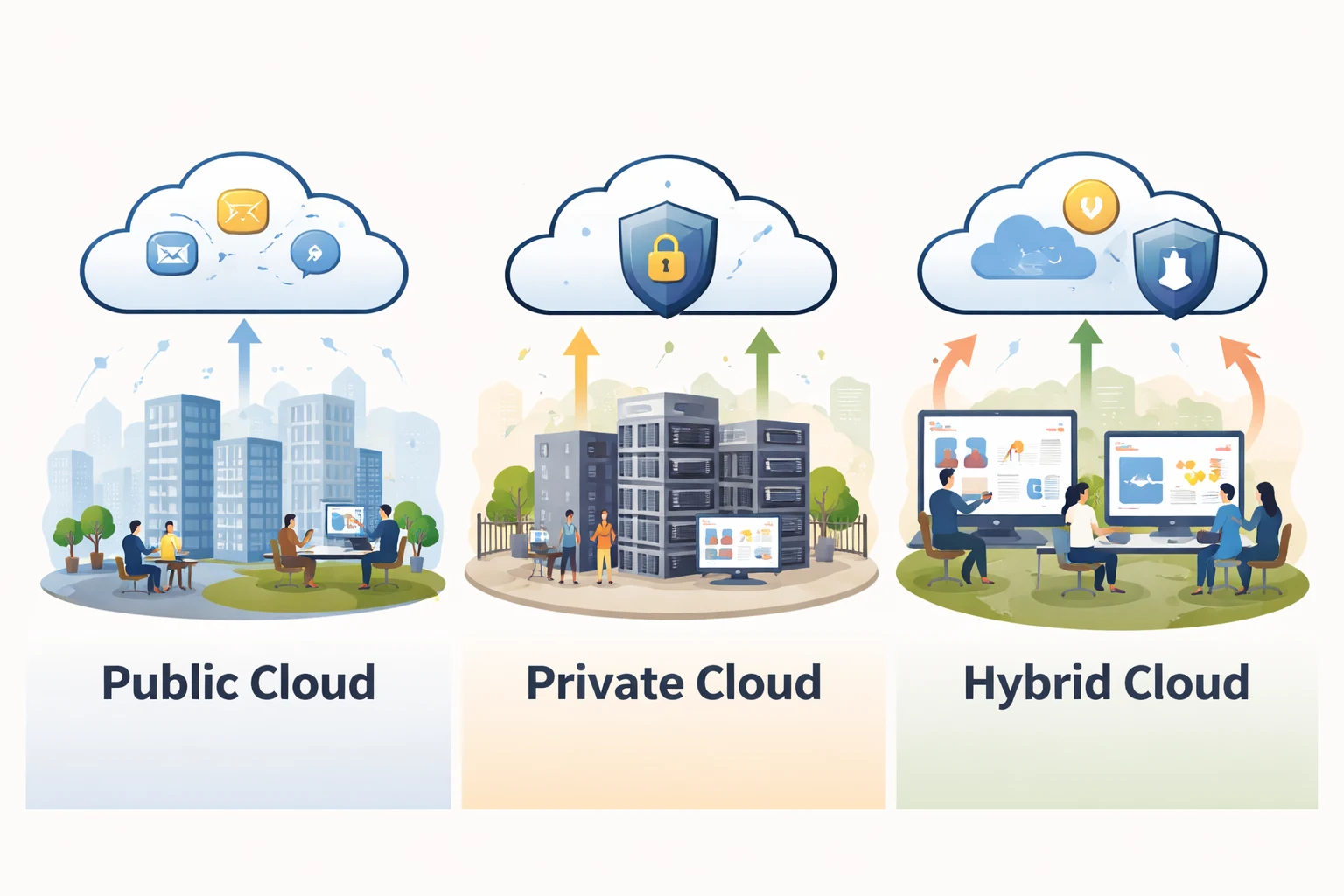
Cloud deployment models define how cloud services are set up and used by a business. Each model offers a different level of cost control, security, and flexibility. Understanding these options helps businesses choose the right cloud structure based on their data needs and growth plans.
Public cloud
The public cloud uses shared infrastructure managed by a cloud service provider. Businesses access computing resources over the internet without managing physical systems. This model is widely used because it is simple, affordable, and easy to scale.
Public cloud works well for businesses that want fast deployment and low operational effort. It reduces IT workload and allows teams to focus on business tasks instead of system maintenance.
- Lower upfront and maintenance costs
- Easy and fast scalability
- Managed entirely by the cloud provider
Private cloud
The private cloud is built for a single organization. It gives businesses more control over data, applications, and security settings. This model is often chosen by companies with strict privacy or compliance requirements.
Private cloud environments can be customized based on business needs. While they may cost more than public cloud solutions, they offer stronger control and predictable performance.
- Greater data control and privacy
- Custom security and compliance settings
- Suitable for sensitive workloads
Hybrid cloud
The hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments. Businesses use the private cloud for critical data and the public cloud for flexible or high-demand tasks. This model creates a balance between control and scalability.
Hybrid cloud helps organizations grow without compromising security. It is useful for businesses that want flexibility while keeping important systems protected.
- Balanced cost and control
- Flexible workload distribution
- Better support for business growth
Choosing the right cloud deployment model allows businesses to use cloud computing more effectively. When these models are understood clearly, cloud computing essentials unlock benefits such as efficiency, security, and long-term stability.
How to Implement Cloud Computing Essentials Step-by-Step
Implementing cloud computing essentials requires planning, clarity, and the right approach. Businesses that move step by step avoid confusion, reduce risk, and get real value from cloud adoption. A structured process helps teams stay focused and make smart decisions from the start.
Assess business needs
Before moving to the cloud, businesses must understand what they actually need. This step helps avoid overspending and wrong service selection.
- Identify workloads such as storage, applications, or collaboration
- Define business goals like cost savings or scalability
- Review current IT systems and limitations
Choose the right cloud service and model
Not every cloud service fits every business. Selecting the right service model and deployment model is critical for success.
- Decide between IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS based on use case
- Choose public, private, or hybrid cloud based on data sensitivity
- Align choices with business size and growth plans
Plan cloud migration carefully
Cloud migration should be organized and controlled. Moving everything at once can create problems, so planning is essential.
- Prioritize which systems move first
- Test applications before full migration
- Minimize downtime and business disruption
Focus on security and access control
Security should be part of the process from day one. Understanding cloud security basics helps protect business data.
- Set clear access permissions
- Protect sensitive data during and after migration
- Follow basic compliance and security practices
Monitor and optimize cloud usage
Cloud implementation does not end after migration. Continuous monitoring ensures long-term efficiency.
- Track resource usage and performance
- Adjust services as business needs change
- Control costs through regular reviews
When businesses follow these steps, cloud computing essentials unlock benefits such as smoother operations, better control, and long-term stability. A planned approach turns cloud adoption into a strategic advantage instead of a technical challenge.
Common Cloud Computing Challenges
Cloud computing can create problems when basics are ignored. Listing these challenges clearly helps businesses stay prepared and avoid common mistakes.
- Cloud cost management
- Paying for unused resources
- No regular usage review
- Poor scaling decisions
- Data security and privacy
- Weak access control
- Poor data handling practices
- Lack of security awareness
- Vendor lock-in
- Overdependence on one provider
- Limited flexibility to switch platforms
- Compatibility issues
- System integration issues
- Difficulty connecting cloud with older systems
- Workflow disruptions
- Data synchronization problems
- Performance and reliability
- Internet dependency
- Unexpected downtime
- Poor backup planning
Understanding these challenges helps businesses plan better. With the right awareness, cloud computing essentials unlock benefits without unnecessary risk or confusion.
Future of Cloud Computing: How Essentials Will Unlock Bigger Benefits

The future of cloud computing depends on how well businesses understand and apply its essentials today. As technology evolves, cloud platforms will support faster decisions, smarter systems, and more efficient operations. Businesses that know the basics will be able to use new tools with confidence instead of struggling to catch up.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Cloud computing provides the power and flexibility that AI systems need to work effectively. When businesses understand cloud essentials, they can use AI tools without complex infrastructure.
- Faster data processing
- Smarter business insights
- Better decision support
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings data processing closer to where data is created. Cloud essentials help businesses combine edge systems with cloud platforms smoothly.
- Reduced delays and faster responses
- Better performance for real-time tasks
- Improved user experience
Automation
Automation uses cloud systems to handle routine tasks with minimal human effort. Understanding cloud basics makes automation easier and more reliable.
- Reduced manual work
- Improved operational efficiency
- Consistent system performance
As cloud technology continues to grow, these innovations will become more common. Businesses that understand cloud computing essentials will unlock bigger benefits by adopting future technologies faster and with less risk.
Cloud Computing Essentials for US Small & Medium Businesses
For small and medium businesses in the United States, cloud computing essentials provide an easy way to use modern technology without heavy cost or complexity. Understanding the basics helps SMBs stay competitive, support daily operations, and grow steadily in a digital-first market.
- Lower technology costs
- Easy scalability as the business grows
- Support for remote and hybrid work
- Better data protection and reliability
- Access to modern cloud-based tools
Cloud computing essentials give US SMBs the flexibility and confidence they need to operate efficiently and plan for long-term success.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become a key part of how modern businesses grow and operate. When companies understand the basics, they make better technology choices and avoid common mistakes. This is how Cloud Computing Essentials Unlock Benefits that support cost control, security, flexibility, and long-term stability.
By learning and applying cloud essentials step by step, businesses can adapt to change, support modern work, and prepare for future technologies with confidence. The cloud is not just a tool. It is a foundation for smarter decisions and sustainable growth in a digital-first world.
FAQs: Cloud Computing Essentials Unlock Benefits
What are the 5 benefits of cloud computing?
The five main benefits of cloud computing are cost savings, easy scalability, better data security, support for remote work, and improved business continuity.
What are the 6 benefits of cloud computing?
Cloud computing provides cost efficiency, scalability, flexibility, strong security, faster deployment, and easier collaboration for businesses.
What are the benefits of learning cloud computing?
Learning cloud computing helps people understand modern technology, improve career skills, reduce IT errors, and use digital tools more effectively.
How do you avoid cloud vendor lock-in?
Businesses can avoid cloud vendor lock-in by planning portability, using common standards, and not relying fully on a single cloud provider.
How cloud computing essentials unlock benefits for businesses?
Cloud computing essentials unlock benefits by helping businesses choose the right services, control costs, improve security, and support long-term growth.



